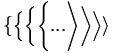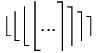VLOS:Viết công thức toán trong VLoS
Mục lục
- 1 TeX
- 2 General
- 3 Functions, symbols, special characters
- 4 Subscripts, superscripts, integrals
- 5 Fractions, matrices, multilines
- 6 Fonts
- 7 Parenthesizing big expressions, brackets, bars
- 8 Spacing
- 9 Align with normal text flow
- 10 Forced PNG rendering
-
11
Examples
- 11.1 Quadratic Polynomial
- 11.2 Quadratic Formula
- 11.3 Tall Parentheses and fractions
- 11.4 Force Rendering
- 11.5 Force Rendering
- 11.6 Integrals
- 11.7 Summation
- 11.8 Differential Equation
- 11.9 Complex numbers
- 11.10 Limits
- 11.11 Integral Equation
- 11.12 Example
- 11.13 Example
- 11.14 Continuation and cases
- 11.15 Example
- 11.16 Example
- 11.17 Gamma Function
- 11.18 Example
- 11.19 Example
- 11.20 Example
- 11.21 Example
- 12 See also
- 13 External links
TeX[sửa]
MediaWiki uses a subset of TeX markup for mathematical formulae. It generates either PNG images or simple HTML markup, depending on user preferences and the complexity of the expression. In the future, as more browsers are smarter, it will be able to generate enhanced HTML or even MathML in many cases.
(More precisely, MediaWiki filters the markup through Texvc, which in turn passes the commands to TeX for the actual rendering. Thus, only a limited part of the full TeX language is supported; see below for details.)
Math markup goes inside <math> ... </math>. The edit toolbar has a button for this.
MediaWiki templates, variables and parameters cannot be used within math tags, see Template talk:Demo of attempt to use parameters within TeX.
The PNG images are black on white (not transparent). These colors, as well as font sizes and types, are independent of browser settings or css. Font sizes and types will often deviate from what HTML renders. The css selector of the images is img.tex.
In the case of a non-white page background, the white background of the formula effectively highlights it, which can be an advantage or a disadvantage.
One may want to avoid using TeX markup as part of a line of regular text, as the formulae don't align properly and the font size, as said, usually does not match.
The alt attribute of the TeX images (the text that is displayed if your browser can't display images; Internet Explorer even shows it up in the hover box) is the wikitext that produced them, excluding the <math> and </math>.
Discussion, bug reports and feature requests should go to the Wikitech-l mailing list. These can also be filed on Mediazilla under MediaWiki extensions.
General[sửa]
Spaces
and
newlines
are
mostly
ignored.
Apart
from
function
and
operator
names,
as
is
customary
in
mathematics
for
variables,
letters
are
in
italics;
digits
are
not.
For
other
text,
(like
variable
labels)
to
avoid
being
rendered
in
italics
like
variables,
use
\mbox
or
\mathrm:
<math>\mbox{abc}</math>
gives
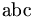
Functions, symbols, special characters[sửa]
For producing special characters without math tags, see Help:Special characters.
Comparison:
-
α
gives
"α"
-
<math>\alpha</math>
gives
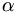 ,
, - ("&" and ";" vs. "\", in this case the same code word "alpha");
-
<math>\alpha</math>
gives
-
√2
gives
"√2"
-
<math>\sqrt{2}</math>
gives
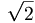
- (the same difference as above, but also another code word, "radic" vs. "sqrt"; in TeX braces);
-
<math>\sqrt{2}</math>
gives
-
√(1-''e''²)
gives
√(1-e²),
-
<math>\sqrt{1-e^2}</math>
gives
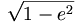 ,
, - (parentheses vs. braces, "''e''" vs. "e", "²" vs. "^2").
-
<math>\sqrt{1-e^2}</math>
gives
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered |
|---|---|---|
| Accents/Diacritics | \acute{a} \quad \grave{a} \quad \breve{a} \quad \check{a} \quad \tilde{a} |
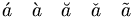 |
| Std. functions (good) |
\sin
x
+
\ln
y
+\operatorname{sgn}
z
\sin
a
\
\cos
b
\
\tan
c
\
\cot
d
\
\sec
e
\
\csc
f |
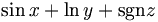
|
| Std. functions (wrong) | sin x + ln y + sgn z |
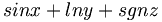 |
| Modular arithmetic |
s_k
\equiv
0
\pmod{m} a \bmod b |
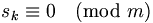
|
| Derivatives | \nabla \; \partial x \; dx \; \dot x \; \ddot y |
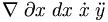 |
|
Sets (Square symbols may not work for some wikis) |
\forall
\;
\exists
\;
\empty
\;
\emptyset
\;
\varnothing
\in
\ni
\not\in
\notin \subset \subseteq \supset \supseteq \cap \bigcap \cup \bigcup \biguplus |
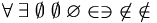
|
| \sqsubset \sqsubseteq \sqsupset \sqsupseteq \sqcap \sqcup \bigsqcup |
 |
|
| Logic | p \land \wedge \; \bigwedge \; \bar{q} \to p \; \lor \vee \; \bigvee \; \lnot \; \neg q \; \setminus \; \smallsetminus |
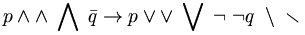 |
| Root | \sqrt{2}\approx 1.4 |
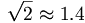 |
| \sqrt[n]{x} |
![{\sqrt[ {n}]{x}}](https://tusach.thuvienkhoahoc.com/images/math/5/e/4/5e4352778f3b156f05ef056f9793ec36.png) |
|
| Relations | \sim \; \approx \; \simeq \; \cong \; \le \; < \; \ll \; \gg \; \ge \; > \; \equiv \; \not\equiv \; \ne \; \propto \; \pm \; \mp |
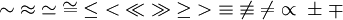 |
| Geometric | \Diamond \; \Box \; \triangle \; \angle \; \perp \; \mid \; \nmid \; \| \; 45^\circ |
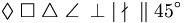 |
|
Arrows (Harpoons may not work for some wikis) |
\leftarrow
\;
\gets
\;
\rightarrow
\;
\to
\;
\leftrightarrow
\longleftarrow
\;
\longrightarrow |
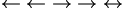
|
| \rightharpoonup \; \rightharpoondown \; \leftharpoonup \; \leftharpoondown \; \upharpoonleft \; \upharpoonright \; \downharpoonleft \; \downharpoonright |
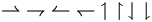 |
|
|
\Leftarrow
\;
\Rightarrow
\;
\Leftrightarrow
\Longleftarrow
\;
\Longrightarrow
\;
\Longleftrightarrow
(or
\iff) |

|
|
| Special |
\eth
\;
\S
\;
\P
\;
\%
\;
\dagger
\;
\ddagger
\;
\star
\;
*
\;
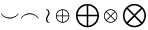
\ldots
\smile
\frown
\wr
\oplus
\bigoplus
\otimes
\bigotimes |
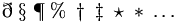
|
| Lowercase \mathcal has some extras | \mathcal {45abcdenpqstuvwx} |
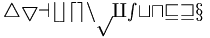 |
Subscripts, superscripts, integrals[sửa]
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HTML | PNG | ||
| Superscript | a^2 |
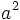 |
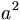 |
| Subscript | a_2 |
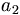 |
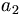 |
| Grouping | a^{2+2} |
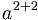 |
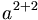 |
| a_{i,j} |
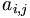 |
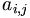 |
|
| Combining sub & super | x_2^3 |
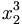 |
|
| Preceding sub & super | {}_1^2\!X_3^4 |
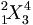 |
|
| Derivative (forced PNG) | x', y'', f', f''\! |
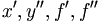 |
|
| Derivative (f in italics may overlap primes in HTML) | x', y'', f', f'' |
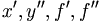 |
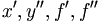 |
| Derivative (wrong in HTML) | x^\prime, y^{\prime\prime} |
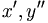 |
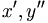 |
| Derivative (wrong in PNG) | x\prime, y\prime\prime |
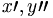 |
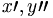 |
| Derivative dots | \dot{x}, \ddot{x} |
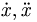 |
|
| Underlines, overlines, vectors | \hat a \ \bar b \ \vec c \ \overrightarrow{a b} \ \overleftarrow{c d} \ \widehat{d e f} \ \overline{g h i} \ \underline{j k l} |
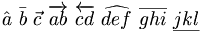 |
|
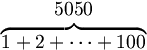
| Overbraces |
\begin{matrix} 5050 \\ \overbrace{ 1+2+\cdots+100 } \end{matrix} |
|
|
| Underbraces |
\begin{matrix} \underbrace{ a+b+\cdots+z } \\ 26 \end{matrix} |
|
|
| Sum | \sum_{k=1}^N k^2 |
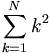 |
|
| Product | \prod_{i=1}^N x_i |
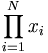 |
|
| Coproduct | \coprod_{i=1}^N x_i |
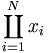 |
|
| Limit | \lim_{n \to \infty}x_n |
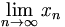 |
|
| Integral | \int_{-N}^{N} e^x\, dx |
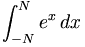 |
|
| Double integral | \iint_{D}^{W} \, dx\,dy |
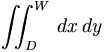 |
|
| Triple integral | \iiint_{E}^{V} \, dx\,dy\,dz |
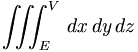 |
|
| Quadruple integral | \iiiint_{F}^{U} \, dx\,dy\,dz\,dt |
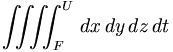 |
|
| Path integral | \oint_{C} x^3\, dx + 4y^2\, dy |
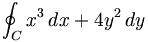 |
|
| Intersections | \bigcap_1^{n} p |
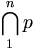 |
|
| Unions | \bigcup_1^{k} p |
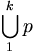 |
|
Fractions, matrices, multilines[sửa]
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fractions | \frac{2}{4} or {2 \over 4} |
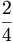 |
||||
| Binomial coefficients | {n \choose k} |
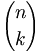 |
||||
| Small Fractions | \begin{matrix} \frac{2}{4} \end{matrix} |
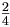 |
||||
| Matrices | \begin{matrix} x & y \\ z & v \end{matrix} |
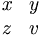 |
||||
| \begin{vmatrix} x & y \\ z & v \end{vmatrix} |
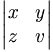 |
|||||
| \begin{Vmatrix} x & y \\ z & v \end{Vmatrix} |
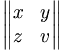 |
|||||
|
\begin{bmatrix}
0
&
\cdots
&
0
\\
\vdots
&
\ddots & \vdots \\ 0 & \cdots & 0\end{bmatrix} |
 |
|||||
| \begin{Bmatrix} x & y \\ z & v \end{Bmatrix} |
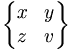 |
|||||
| \begin{pmatrix} x & y \\ z & v \end{pmatrix} |
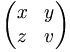 |
|||||
| Case distinctions | f(n) = \begin{cases} n/2, & \mbox{if }n\mbox{ is even} \\ 3n+1, & \mbox{if }n\mbox{ is odd} \end{cases} |
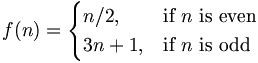 |
||||
| Multiline equations | \begin{matrix}f(n+1) & = & (n+1)^2 \\ \ & = & n^2 + 2n + 1 \end{matrix} |
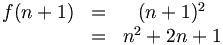 |
||||
| Alternative multiline equations (using tables) |
{|
|-
|<math>f(n+1)</math>
|<math>=(n+1)^2</math>
|-
|
|<math>=n^2 + 2n + 1</math>
|}
|
|
Fonts[sửa]
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
(Note the lack of omicron; note also that several upper case Greek letters are rendered identically to the corresponding Roman ones) |
\Alpha\
\Beta\
\Gamma\
\Delta\
\Epsilon\
\Zeta\
\Eta\
\Theta\
\Iota\
\Kappa\
\Lambda\
\Mu\
\Nu\
\Xi\
\Pi\
\Rho\
\Sigma\
\Tau\
\Upsilon\
\Phi\
\Chi\
\Psi\
\Omega |
|
|
| \mathbb{N}\ \mathbb{Z}\ \mathbb{Q}\ \mathbb{R}\ \mathbb{C} |
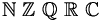 |
||
| (vectors) | \mathbf{x}\cdot\mathbf{y} = 0 |
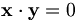 |
|
| boldface (greek) | \boldsymbol{\alpha} + \boldsymbol{\beta} + \boldsymbol{\gamma} |
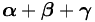 |
|
| italics | \mathit{ABCDE abcde 1234} |
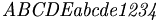 |
|
| \mathrm{ABCDE abcde 1234} |
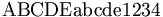 |
||
| \mathfrak{ABCDE abcde 1234} |
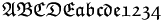 |
||
| Calligraphy/Script | \mathcal{ABCDE abcde 1234} |
 |
|
| \aleph \beth \gimel \daleth |
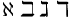 |
||
| non-italicised characters | \mbox{abc} |
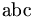 |
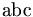 |
| mixed italics (bad) | \mbox{if} n \mbox{is even} |
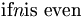 |
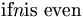 |
| mixed italics (good) | \mbox{if }n\mbox{ is even} |
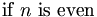 |
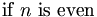 |
Parenthesizing big expressions, brackets, bars[sửa]
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered |
|---|---|---|
| Bad | ( \frac{1}{2} ) |
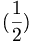 |
| Good | \left ( \frac{1}{2} \right ) |
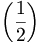 |
You can use various delimiters with \left and \right:
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Parentheses | \left ( \frac{a}{b} \right ) |
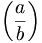 |
|
| Brackets | \left [ \frac{a}{b} \right ] \quad \left \lbrack \frac{a}{b} \right \rbrack |
![\left[{\frac {a}{b}}\right]\quad \left\lbrack {\frac {a}{b}}\right\rbrack](https://tusach.thuvienkhoahoc.com/images/math/7/c/b/7cb5a74153ec87cdda6b92669ba685e1.png) |
|
| Braces | \left \{ \frac{a}{b} \right \} \quad \left \lbrace \frac{a}{b} \right \rbrace |
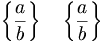 |
|
| Angle brackets | \left \langle \frac{a}{b} \right \rangle |
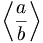 |
|
| Bars and double bars | \left | \frac{a}{b} \right \vert \left \Vert \frac{c}{d} \right \| |
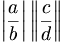 |
|
| Floor and ceiling functions: | \left \lfloor \frac{a}{b} \right \rfloor \left \lceil \frac{c}{d} \right \rceil |
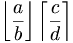 |
|
| Slashes and backslashes | \left / \frac{a}{b} \right \backslash |
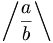 |
|
| Up, down and up-down arrows | \left \uparrow \frac{a}{b} \right \downarrow \quad \left \Uparrow \frac{a}{b} \right \Downarrow \quad \left \updownarrow \frac{a}{b} \right \Updownarrow |
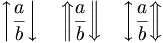 |
|
|
Delimiters
can
be
mixed, |
\left
[
0,1
\right
) |
|
|
|
Use
\left.
and
\right.
if
you
don't want a delimiter to appear: |
\left . \frac{A}{B} \right \} \to X |
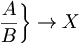 |
|
| Size of the delimiters | \big( \Big( \bigg( \Bigg( ... \Bigg] \bigg] \Big] \big] |
|
|
| \big\{ \Big\{ \bigg\{ \Bigg\{ ... \Bigg\rangle \bigg\rangle \Big\rangle \big\rangle |
|
||
| \big\| \Big\| \bigg\| \Bigg\| ... \Bigg| \bigg| \Big| \big| |
 |
||
| \big\lfloor \Big\lfloor \bigg\lfloor \Bigg\lfloor ... \Bigg\rceil \bigg\rceil \Big\rceil \big\rceil |
|
||
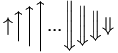
| \big\uparrow \Big\uparrow \bigg\uparrow \Bigg\uparrow ... \Bigg\Downarrow \bigg\Downarrow \Big\Downarrow \big\Downarrow |
|
||
Spacing[sửa]
Note that TeX handles most spacing automatically, but you may sometimes want manual control.
| Feature | Syntax | How it looks rendered |
|---|---|---|
| double quad space | a \qquad b |
 |
| quad space | a \quad b |
 |
| text space | a\ b |
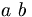 |
| text space without PNG conversion | a \mbox{ } b |
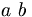 |
| large space | a\;b |
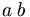 |
| medium space | a\>b | [not supported] |
| small space | a\,b |
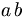 |
| no space | ab |
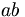 |
| small negative space | a\!b |
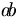 |
Align with normal text flow[sửa]
Due to the default css
img.tex { vertical-align: middle; }
an
inline
expression
like
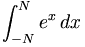 should
look
good.
should
look
good.
If you need to align it otherwise, use <font style="vertical-align:-100%;"><math>...</math></font> and play with the vertical-align argument until you get it right; however, how it looks may depend on the browser and the browser settings.
Forced PNG rendering[sửa]
To force the formula to render as PNG, add \, (small space) at the end of the formula (where it is not rendered). This will force PNG if the user is in "HTML if simple" mode, but not for "HTML if possible" mode (math rendering settings in preferences).
You can also use \,\! (small space and negative space, which cancel out) anywhere inside the math tags. This does force PNG even in "HTML if possible" mode, unlike \,.
This could be useful to keep the rendering of formulae in a proof consistent, for example, or to fix formulae that render incorrectly in HTML (at one time, a^{2+2} rendered with an extra underscore), or to demonstrate how something is rendered when it would normally show up as HTML (as in the examples above).
For instance:
| Syntax | How it looks rendered |
|---|---|
| a^{c+2} |
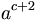 |
| a^{c+2} \, |
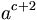 |
| a^{\,\!c+2} |
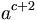 |
| a^{b^{c+2}} |
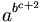 (WRONG
with
option
"HTML
if
possible
or
else
PNG"!)
(WRONG
with
option
"HTML
if
possible
or
else
PNG"!) |
| a^{b^{c+2}} \, |
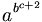 (WRONG
with
option
"HTML
if
possible
or
else
PNG"!)
(WRONG
with
option
"HTML
if
possible
or
else
PNG"!) |
| a^{b^{c+2}}\approx 5 |
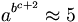 (due
to
"
(due
to
"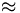 "
correctly
displayed,
no
code
"\,\!"
needed) "
correctly
displayed,
no
code
"\,\!"
needed) |
| a^{b^{\,\!c+2}} |
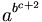 |
| \int_{-N}^{N} e^x\, dx |
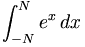 |
| \int_{-N}^{N} e^x\, dx |
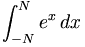 |
| \int_{-N}^{N} e^x\, dx |
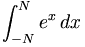 |
This
has
been
tested
with
most
of
the
formulae
on
this
page,
and
seems
to
work
perfectly.
You might want to include a comment in the HTML so people don't "correct" the formula by removing it:
- <!-- The \,\! is to keep the formula rendered as PNG instead of HTML. Please don't remove it.-->
Examples[sửa]
Quadratic Polynomial[sửa]
<math>x_1 = a^2 + b^2 + c^2 \,</math>
Quadratic Formula[sửa]
<math>x_{1,2}=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt{b^2-4ac}}{2a}</math>
Tall Parentheses and fractions[sửa]
<math>2 = \left( \frac{\left(3-x\right) \times 2}{3-x} \right)</math>
Force Rendering[sửa]
<math>4-2x = 9-3x \!</math>
Force Rendering[sửa]
<math>-2x+3x = 9-4 \!</math>
Integrals[sửa]
<math>\int_a^x \int_a^s f(y)\,dy\,ds = \int_a^x f(y)(x-y)\,dy</math>
Summation[sửa]
<math>\sum_{m=1}^\infty\sum_{n=1}^\infty\frac{m^2\,n} {3^m\left(m\,3^n+n\,3^m\right)}</math>
Differential Equation[sửa]
<math>u'' + p(x)u' + q(x)u=f(x),\quad x>a</math>
Complex numbers[sửa]
<math>|\bar{z}| = |z|, |(\bar{z})^n| = |z|^n, \arg(z^n) = n \arg(z)\,</math>
Limits[sửa]
<math>\lim_{z\rightarrow z_0} f(z)=f(z_0)\,</math>
Integral Equation[sửa]
<math>\phi_n(\kappa) = \frac{1}{4\pi^2\kappa^2} \int_0^\infty \frac{\sin(\kappa R)}{\kappa R} \frac{\partial}{\partial R}\left[R^2\frac{\partial D_n(R)}{\partial R}\right]\,dR</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>\int_0^\infty x^\alpha \sin(x)\,dx = 2^\alpha \sqrt{\pi}\, \frac{\Gamma(\frac{\alpha}{2}+1)}{\Gamma(\frac{1}{2}-\frac{\alpha}{2})}</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>\phi_n(\kappa) = 0.033C_n^2\kappa^{-11/3},\quad \frac{1}{L_0}\ll\kappa\ll\frac{1}{l_0}\,</math>
Continuation and cases[sửa]
f(x) = \begin{cases}1 & -1 \le x < 0\\ \frac{1}{2} & x = 0\\x&0<x\le 1\end{cases}
Example[sửa]
<math>J_p(z) = \sum_{k=0}^\infty \frac{(-1)^k\left(\frac{z}{2}\right)^{2k+p}}{k!\Gamma(k+p+1)}\,</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>{}_pF_q(a_1,...,a_p;c_1,...,c_q;z) = \sum_{n=0}^\infty \frac{(a_1)_n\cdot\cdot\cdot(a_p)_n}{(c_1)_n\cdot\cdot\cdot(c_q)_n}\frac{z^n}{n!}\,</math>
Gamma Function[sửa]
<math>\Gamma(n+1) = n \Gamma(n),\quad n>0</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>\int_0^1 \frac{1}{\sqrt{-\ln x}}\,dx</math>
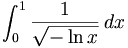
Example[sửa]
<math>\int_0^\infty e^{-st}t^{x-1}\,dt,\quad s>0</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>B(u) = \sum_{k=0}^N {P_k}{N! \over k!(N - k)!}{u^k}(1 - u)^{N-k}\,</math>
Example[sửa]
<math>u(x,y) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi}}\int_0^\infty f(\xi)\left[g(|x+\xi|,y)+g(|x-\xi|,y)\right]\,d\xi</math>
See also[sửa]
- Typesetting of mathematical formulas
- Proposed GNU LilyPond support
- Table of mathematical symbols
- Blahtex, or blahtex: a LaTeX to MathML converter for Wikipedia
- General help for editing a Wiki page
External links[sửa]
- A LaTeX tutorial. http://www.maths.tcd.ie/~dwilkins/LaTeXPrimer/
- A PDF document introducing TeX -- see page 39 onwards for a good introduction to the maths side of things: http://www.ctan.org/tex-archive/info/gentle/gentle.pdf
- A PDF document introducing LaTeX -- skip to page 59 for the math section. See page 72 for a complete reference list of symbols included in LaTeX and AMS-LaTeX. http://www.ctan.org/tex-archive/info/lshort/english/lshort.pdf
- TeX reference card: http://www.csit.fsu.edu/~mimi/tex/tex-refcard-letter.pdf
- http://www.ams.org/tex/amslatex.html
- A set of public domain fixed-size math symbol bitmaps: http://us.metamath.org/symbols/symbols.html
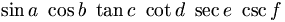
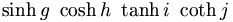
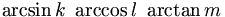
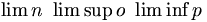
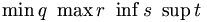
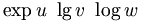
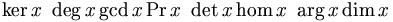
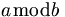

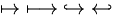
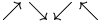

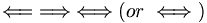
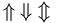
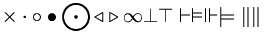
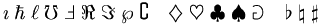
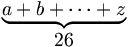
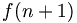
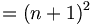
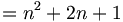
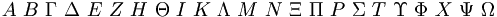
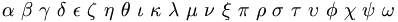
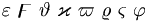
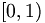
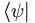
![{\big (}{\Big (}{\bigg (}{\Bigg (}...{\Bigg ]}{\bigg ]}{\Big ]}{\big ]}](https://tusach.thuvienkhoahoc.com/images/math/0/a/2/0a2c41697f07213ddaa59a92738e8bd6.png)